Internet of Things or IoT devices are increasingly influencing the way we do business and the way we live. In this article, we will demonstrate how IoT devices use edge computing to personalize the handling of your data. This process will help you get the most out of your IoT devices no matter where you are.
If you are new here and the above introduction confuses you a bit about a concept like IoT. You can find a lot of other articles on this topic on our blog. In the rest, we’ll cover the IoT, explain edge computing, types of edge computing, like fog computing, and give examples where you might find yourself in it. Great, let’s talk a little bit about IoT.
1. IoT Overview
IoT or a fully written Internet of Things is a system of devices that can interact with each other on data through the internet. The three main components of IoT are device, gateway, and storage cloud. In it, users will interact with IoT devices while they also interact with each other. Data from these devices through the gateway goes to a powerful storage back-end, like the cloud. At the cloud, these data will be analyzed and stored to create insights to help IoT devices optimize all your experiences.
Here is an example for you. You are a camera shop owner who knows how to catch the trend. Your product is not a mediocre camera, they are cameras designed to function as IoT devices. Every time a customer takes a photo, the data will be sent to the cloud, where, in addition to storage, analysis, and suggestions to help the photo look better come to the customer. Great, this IoT device has made you a thriving business person.
Taking advantage of the opportunity, you launch a device that not only takes photos but also has the ability to record high-resolution video. This is where things get more complicated. You quickly realize, the videos sent to the cloud will have a larger capacity, higher resolution, so it takes longer to process them. At cloud, processing these videos takes a lot more effort and time than photos. Customers, of course, won’t be happy, once they’ve gotten used to the quick experience of taking pictures. So how can you continue this great business idea without sacrificing customer satisfaction? The answer we can give you is edge computing. What is the solution like? We will introduce it now.
2. What is edge computing?
Edge computing, as the name implies, is computing at the edge. You can fully understand it as a system of distributed resources and applications near where data is generated in order to process them there instead of moving them to a data center, like the cloud [2]. There are two main types of edge computing. One is to use the computing power of the devices themselves, called edge devices. Or you can create some more infrastructure close to the device, so that the data can be processed quickly, instead of sending it to the cloud, let’s call it an edge server. How it works will be discussed with you in more detail when we talk about types of edge computing. This improves business through many aspects such as faster delivered insights, significantly improved response times, and more efficient use of network capacity.
Is it possible to let IoT devices do the computations that are done by cloud or AI? Are there 2 possible explanations for this question?
First, the capabilities of cloud or AI, even though powerful, are still not enough to meet the computing needs of the huge amounts of data generated by hundreds of thousands or even millions of devices. Gartner predicts that 10% of data handled by enterprises outside of a traditional data center or cloud will increase to 75% by 2025 [3]. This shows that devices handle data on their own, and the need for the necessity of mitigating the transfer of data to the cloud. One reason that should be stated is that much of the data currently from is underutilized. Research published by McKinsey & Company shows that an offshore oil rig has 30,000 sensors that generate data but direct decisions are made based on only nearly one percent of the data from those sensors [4]. That means there is a lot of data that needs to be processed quickly.
Second, 5G network infrastructure and computing capabilities of IoT devices are growing. Obviously, with current 4G networks and IoT devices, you can still realize edge computing, but it’s their visible growth that brings real power. IBM says that with a car with about 50 CPUs today, a lot of things we can do that we couldn’t do before. IBM also said that the 15 billion devices on the market today will grow to 55 billion by 2022 and 150 billion by 2025 [1]. This represents a tremendous amount of data, and massive computing power from devices is gradually available.
We all agree that edge computing is a great solution for processing big data quickly, with low latency. But more specifically, how are we going to do this? We categorize the types of it, according to Cisco [5], in the next part.
3. Types of edge computing
- 1. Fog computing:
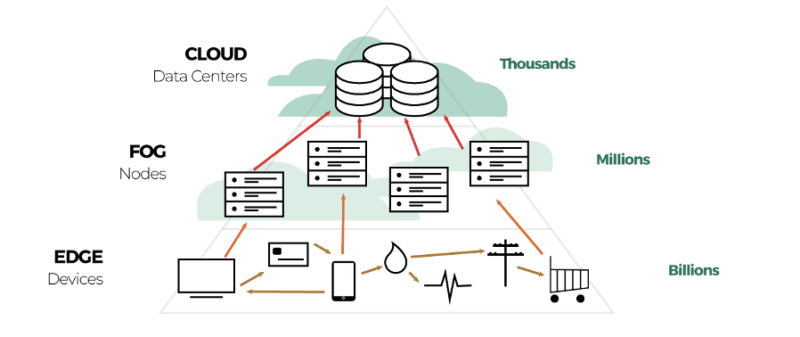 Design of fog computing. Source: e-zigurat
Design of fog computing. Source: e-zigurat
(https://www.e-zigurat.com/innovation-school/blog/cloud-edge-fog-computing-practical-applications/)
This is the most practical application of the concept of edge computing. Fog means you don’t need to go to the cloud to process the data, you just need to go to the fog. This means decentralizing infrastructure through placing nodes between the cloud and the strategic edge, to scale, increase processing capacity, and reduce data transmission time. Cisco calls this “bringing the cloud to the ground” [5].
3.2. Multi-access Computing (MEC):
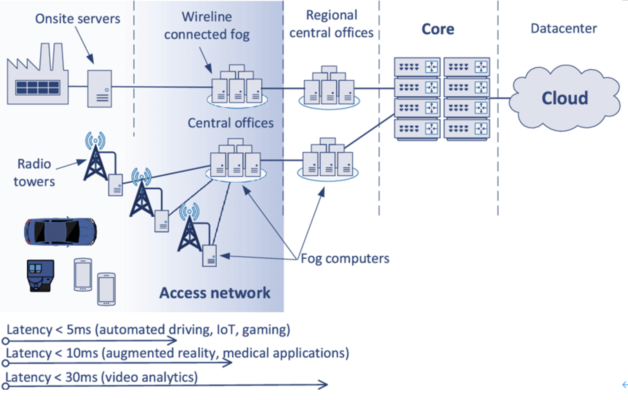 Design of Multi-access Computing (MEC). Source: researchgate
Design of Multi-access Computing (MEC). Source: researchgate
(https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Multi-access-edge-computing-architecture_fig1_333468214)
The development of 5G networks provides large amounts of bandwidth and low latency, which takes us further in designing edge computing. Content providers and application developers can design strategic edges by arbitrarily choosing the location of computing points near the device, or in other words, on the network. This allows us to make the most of real-time access and keep latency to a minimum.
3.3. Micro data center:
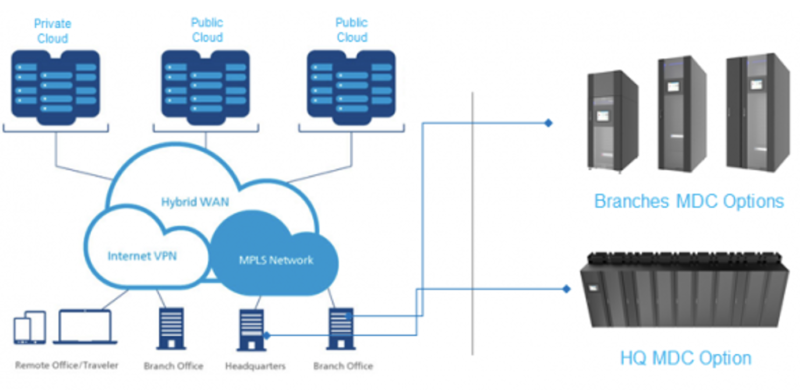 Design of Micro data center. Source: https://blogspot.attom.tech/2019/08/micro-data-center-future-ready-choice.html?showComment=1617948228521
Design of Micro data center. Source: https://blogspot.attom.tech/2019/08/micro-data-center-future-ready-choice.html?showComment=1617948228521
When you need a more flexible data center to quickly deploy to critical areas, you can choose the Microdata center model. This model gives you micro centers that have similar components to conventional data centers but are more robust, flexible, and closer to where the data comes from.
3.4. Cloudlets:
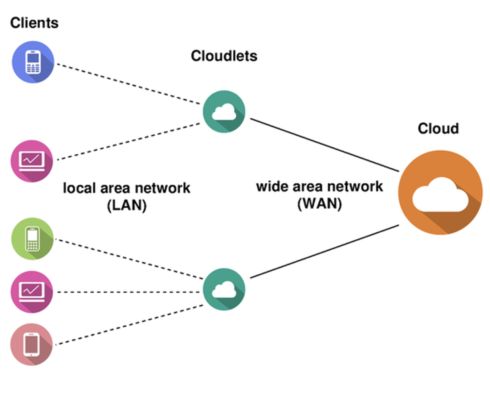 Design of Cloudlet. Source: hecustomizewindows
Design of Cloudlet. Source: hecustomizewindows
(https://thecustomizewindows.com/2020/05/what-is-a-cloudlet-in-cloud-computing/)
Cloudlets are all about portability. They are modeled like a cloud but are designed to help mobile apps, especially those that are resource-intensive, interactive, and need low latency.
3.5. Emergency response unit:
This model is designed to rescue users in an emergency situation with the goal of re-establishing communication for the affected area. The model that wants to work well needs to be run by a skilled team and needs to be deployed quickly.
4. Benefits of edge computing
It is part of a larger ecosystem with unprecedented potential benefits. Some of the immediate benefits include:
4.1. Increase speed and reduce latency
As the most obvious benefit, reducing response latency and increasing the speed of user interaction.
4.2. Information security
Some may suspect that moving to compute and storage out of the data center could create a security hole. In fact, many solutions have been implemented to help edge computing still keep the information it stores secure, and some are even better than before.
4.3. Save money on the investment
You don’t need to transfer all your data to a traditional hub which means you can save money. The flexibility of edge computing allows you to take advantage of this technology at every stage of your business without breaking the bank.
4.5. Continuity
Edge devices are designed and operated to ensure continuity and transparency to best serve you.
4.6. Flexibility and scalability
The many types of edge computing and their broad applications that we present to you are a powerful demonstration of how flexible and scalable it can be.
5. Examples of edge computing
I hope you have not forgotten the example of the video camera store in the beginning that we introduced. Let’s have a look at more examples here. We found an interesting exchange of experts from various fields sharing with IBM about the future of edge computing [6]. We would like to present you great examples from them in 3 fields: retail, finance, and telecommunications:
5.1. Retail industry:
The great thing about edge computing in the retail industry is the personalization of the user’s shopping experience. The vast amount of data collected from your store allows you to know exactly what your customers want and need. Because you have hundreds of them and thousands of guests. It’s hard to do this alone. It not only provides solutions but also saves you costs through flexibility and scalability. At every point of your business, depending on what you have and what you need, there is always the right software that can assist you.
5.2. Financial services:
What would an ATM look like with more edge computing? They are capable of processing streaming data like never before by analyzing risks from cameras in ATM booths and alerting to anomalies from withdrawals. This is a prime example of the application of edge computing to the financial industry. Low latency and blazing-fast analytics enable you to make data-driven decisions within milliseconds.
5.3. Telcos (Telecommunications company):
As we mentioned, you can absolutely use 4G networks to realize edge computing, but it’s the 5G network that opens up the most uses you’ve ever seen. It can be said that the 5G network is the raw material of edge computing. Telecom businesses can take advantage of this opportunity to accelerate digital transformation, improve end-user experience, and unlock the available potential of the cloud. This is really a process that helps them reduce operating costs while still increasing profits, improving business operations, user interaction, and reinvesting in production.
6. Conclusion
We are truly grateful that you are still here with us until the end. This shows that you are really interested in edge computing. If you are skeptical about their application, there are tons of examples out there we can tell you such as cloud gaming technology, intelligent traffic control, autonomous vehicles, new ways of transportation. , …. Even if these examples still don’t satisfy you, don’t worry, because we’re here to help you at any stage of edge computing. We present this technology to you with the excitement of the present and look forward to welcoming the bright future with you. Whenever we are ready with you, tell your success story to the rest of the world.
