1. IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) defines the network of physical objects including sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of data connection, exchange, and communication over the internet with other devices and systems. These gadgets range with sophisticated industrial tooling from basic home items.
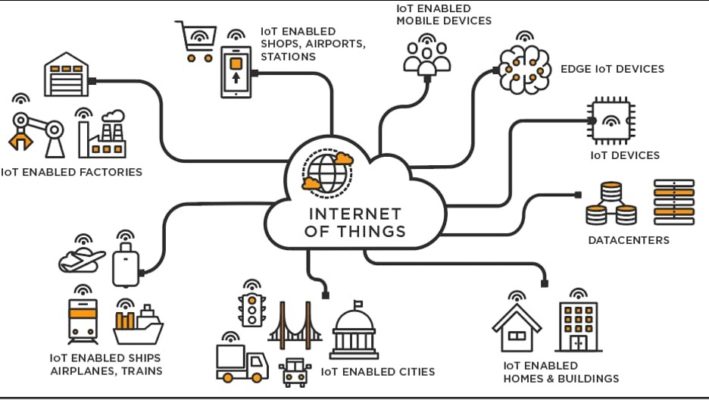
Fig.1: Description image for IoT (Source: https://www.tibco.com/reference-center/what-is-iot)
The confluence of several technologies, real-time analysis, machine learning, all-around computing, commodity sensors, and embedded systems has brought developments. Things have developed. Traditional fields in the realm of embedded systems (including home and building automation), wireless sensor networks, control systems, etc. all contribute to the Internet of things. IoT technology on the consumer market is most commonly synonymous with products related to the “smart home” concept that support one or more common ecosystems, including appliances and devices (for example, lighting systems, thermostats, homeland security systems, cameras, and other home appliances), and may be controlled via devices such as smart phones and smart speakers linked with that ecosystem. In healthcare systems, IoT may also be employed.
Several major concerns are raised regarding hazards in the expansion of IoT, in particular in privacy and security, and the business and government have thus begun to address these problems, including developing international standards.
2. Smart Grid
The Smart Grid is a unique chance to transform the energy sector into a new age of dependability, availability, and efficiency, which will contribute to our economic and environmental health. It will be essential throughout the transition phase to test, technological advancements, consumer education, standards, and regulatory development, and the exchange of information amongst projects in order to ensure that the advantages that we see from the Smart Grid are made true. The advantages of the Smart Grid are.
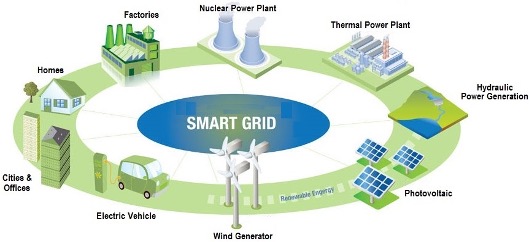
Fig.2: Description image for Smart Grid (Source: https://electricalbaba.com/smart-grid-an-overview/)
Smart Grid technology contributes to the efficient and presently unfitting energy management solutions of the IoT system. It’s the two-way communication among linked devices and hardware that can understand and respond to the user requirements that makes IoT Smart Grid superior. These technologies make an intelligent grid more robust than the present electricity system and less expensive.
- The benefits of smart grid in IoT:
- Intelligent use of energy
- Cleaner Use of Energy
- Bass fees
- Enhanced parking and transportation
- Assistance in the management of waste and water
The smart grid is part of an IoT framework to monitor and control everything remotely – lights, road signs, congestion, car parks, road alerts, and the early identification of things like power inflow due to terrible weather and earthquakes. This is achieved through the Smart Grid using a network of transmission lines, intelligent meters, distribution automation, substation, transformers, sensors, software, and more dispersed to companies and residences around the city.
3. Energy Management
Energy management of energy production and consumption planning and operation and energy supply and storage. energy management. The aims are to save resources, protect the climate, and to save costs while consumers permanently have access to the energy they need. Environmental, production, logistics, and other established business operations are intimately related, as well as proactive, structured and systematic energy usage management of buildings or organizations satisfy both environmental and economic needs.

Fig.3: Description image for Energy Management(Source: https://www.viatech.com/en/solutions/smart-industry/energy-management/)
IoT energy management is a process including energy consumption planning and management in many sectors. Energy management Internet of Things aims at monitoring and optimizing energy compliance, improved capacity use, improved business productivity, reduced maintenance and labor, and increased energy asset dependability.
- The benefits of energy management in IoT:
- Reduce energy consumption
- Reduce emissions of carbon
- Improved regulatory compliance
- Green energy integration
- Maintenance of assets
How the Internet of Things technology helps save energy:
- Intelligent light, air conditioning, temperature control
- Systems for energy management
- Solutions on green energy
- Storage of energy
- Plants, wind, and solar connected stations connected
Source:
https://www.oracle.com/internet-of-things/what-is-iot/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smart_grid
https://www.smartgrid.gov/the_smart_grid/smart_grid.html
https://www.telit.com/blog/iot-smart-grid-benefits/#:~:text=The%20Smart%20Grid%20is%20part,of%20earthquakes%20and%20extreme%20weather.
https://igzy.com/blog/iot-energy management/#:~:text=IoT%20Energy%20Management%20is%20a,consumption%20patterns%20in%20different%20industries.&text=These%20solutions%20can%20be%20utilized,most%20fundamental%20and%20granular%20level.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_management
