IoT is considered one of the most successful technologies. The continuous development helps connect millions of smart devices every day, which is strongly demonstrated in the forwarding, receiving and processing of data. To ensure IoT success, quality of service (QoS) assurance is used to mitigate limitations from equipment and network infrastructure. QoS improves end-to-end latency, network throughput, network and packet delivery rates. The growth of IoT devices brings security requirements. In this article, we clarify how to use QoS-optimal to increase the security of IoT devices.
1. IoT Security Challenges
We are not talking about IoT in depth. Readers can find more articles on this topic at Speranza’s blog. In short, IoT is a system of connecting and monitoring devices through the internet. To operate the IoT system well, the time factor needs to be carefully considered. The response time of IoT applications needs to be fast and constant to satisfy the users. Therefore, people use lossless transmission methods and architectures such as fog computing, edge computing (including virtual network nodes to reduce network latency). However, this very approach causes some problems for IoT security. The security practices of the internet cannot be directly applied to IoT. Therefore, it is necessary to use advanced techniques such as QoS for more security for IoT. Research by scientists from Kalinga University, India [1] shows the essential security elements of IoT devices:
 Fig1: Security requirements that IoT devices should have. Made with Canva. Content from: https://www.ijeat.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v9i2/B3757129219.pdf
Fig1: Security requirements that IoT devices should have. Made with Canva. Content from: https://www.ijeat.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v9i2/B3757129219.pdf
2. What is QoS or Quality of Service?
2.1. Overview of QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) is a mechanism that controls traffic and regulates overall network traffic by prioritizing applications that need network priority. By using QoS, applications can be greatly improved on the network, specifically in terms of speed, latency, loss, and packet transmission. QoS can be used for IoT applications, applications for watching movies, online meetings, video calls, etc. [2]
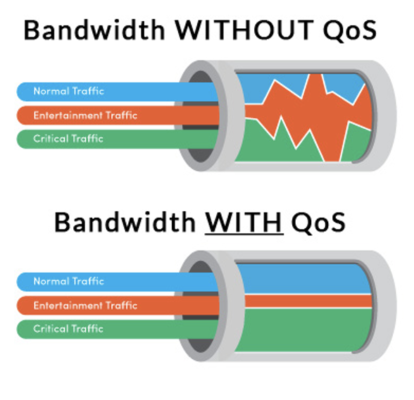
Fig2: Bandwidth without QoS vs. Bandwidth with QoS. Source: https://blogs.salleurl.edu/en/qos-datacenters
2.2. How does QoS work?
Have you ever taken the bus rapid transit (BRT) route? When there is a traffic jam, the BRT can still move thanks to its own lane. QoS networking technology works similarly by creating separate virtual queues for applications, based on a predefined priority. With QoS, the network administrator has the power to specify the order in which packets are processed determining the priority of the application. [3]
Thanks to the above operations, QoS can improve network traffic types. Types of network traffic you need to know:
- Bandwidth: The speed of the link. QoS can handle different bandwidths for different priority applications.
- Latency: The time it takes for a packet to travel from source to final destination. QoS improves latency by creating virtual queues.
- Loss: Data is lost during packet transfer. QoS allows the administrator to decide which packets to drop in case of need
- Jitter: When the network is congested resulting in packets being transported at unequal rates causing them to arrive at their destination out of order. IoT applications cannot function if this situation occurs frequently. QoS can limit this.
2.3. Advantages of QoS in IoT Security
- Improve bandwidth, latency; reduce loss, jitter: The way QoS works improves network transmission, making security easier.
- Send alerts quickly and efficiently: thanks to QoS, IoT applications can send alerts quickly and accurately. Selecting priorities also streams critical alerts to any point in time
- Reduce equipment by optimizing the network: when the transmission line is optimized, the network nodes can be reduced while still meeting the needs of use and security.
- Cost savings: not so much related to security, but by reducing devices, costs will also be reduced, but the quality of security is enhanced.
3. QoS Optimization: a step forward for IoT security!
3.1. Ideas about QoS optimization
QoS is good, this is very true for IoT. But QoS was not created for security purposes, but to improve network traffic. Therefore, it is necessary to combine QoS with other technologies to enhance comprehensive security. The architecture of IoT consists of 3 main components: application layer, network layer, perception layer.
 Fig4: 3 components of the architecture of IoT. Source: https://www.netburner.com/learn/architectural-frameworks-in-the-iot-civilization/
Fig4: 3 components of the architecture of IoT. Source: https://www.netburner.com/learn/architectural-frameworks-in-the-iot-civilization/
Many studies suggest that QoS solutions are used to improve security performance at all three layers, but for the best effect, researchers often use QoS optimization to improve security at the network layer. There are many ways to optimize QoS, depending on the purpose. We present to you a study from the sciences from Kalinga University, India. They use an IoT architecture that is typical of fog computing because of its enhanced security capabilities. The weakness of fog computing is that the network lines at virtual nodes can be attacked, the use of QoS and techniques such as machine learning, cognitive radio networks (CRNs) improve this well.
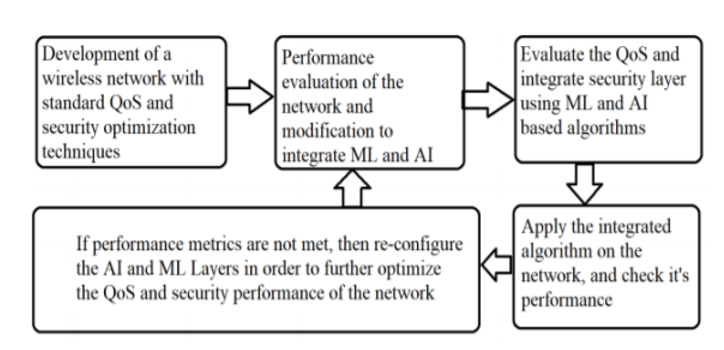 Fig5: Step to apply QoS Optimization in IoT security. Source: https://www.ijeat.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v9i2/B3757129219.pdf
Fig5: Step to apply QoS Optimization in IoT security. Source: https://www.ijeat.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v9i2/B3757129219.pdf
3.2. Security application of QoS optimization in practice
Also according to the study, the areas where security techniques from QoS optimization can be applied can be banking, military and healthcare.
- Banking: Data in financial industries like banking is extremely important and protected. These are also valuable data that hackers can attack, especially when data from IoT is increasing and revealing weaknesses. Proposing solutions like QoS optimization can help banks secure customer information.
- Military: More and more devices in the military are IoT devices. The use of IoT in the military field is inevitable because of its synchronization, speed and high efficiency. IoT can be an influence on intelligence operations. When these IoT data are related to national security, it is necessary to keep them as secure as possible.
- Healthcare: telemedicine services need the service of IoT devices. IoT appears more and more in the medical field, which means it stores more and more personal information of patients. So it is necessary to secure healthcare IoT devices.
4. Conclusion
Security in IoT is essential, from protecting patient information to protecting national security. In business operations, good security gives you deep trust from your customers and a solid foundation for bold business ideas. If you are hesitant with IoT because of security concerns, this article is a suggestion for you on how to do great business with IoT without worrying about security. If you have any concerns, we are always by your side, ready to help you.
