Devices and networks connected to the internet of things are protected by IoT security (IoT). Computer devices, mechanical and digital equipment, items, animals, and/or humans are connected to the internet through IoT. There are unique identifiers for each “thing,” as well as the capacity to automatically transfer data via a network. As long as gadgets are not adequately protected, they are vulnerable to a range of significant vulnerabilities. As a result of many high-profile incidents, IoT security has become increasingly important. For networks with IoT devices attached, this is important. Technology, approaches, protocols, and activities can be used to minimize the growing IoT vulnerabilities of modern organizations.
What is IoT Security?
 Source: https://532386f9a72d1dd857a8-41058da2837557ec5bfc3b00e1f6cf43.ssl.cf5.rackcdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Depositphotos_250147614_s-2019.jpg
Source: https://532386f9a72d1dd857a8-41058da2837557ec5bfc3b00e1f6cf43.ssl.cf5.rackcdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Depositphotos_250147614_s-2019.jpg
The techniques of protection employed to protect internet-connected or network-based devices are referred to as IoT security. The phrase Internet of Things (IoT) is quite wide, and as technology continues to advance, the word has only become larger. Almost every electronic item may communicate with the internet or other devices in some way.
IoT security refers to the approaches, strategies, and technologies that are utilized to keep these devices from getting hacked. Ironically, the connection inherent in IoT devices exposes them to hackers.
Due to the wide scope of IoT, IoT security is much more extensive. As a result, a wide range of techniques now falls under the purview of IoT security. They are just a few of the strategies that IT executives may employ to address the rising danger of cybercrime and cyberterrorism rooted in insecure IoT devices.
Internet of Things (IoT) security concerns
A threat actor’s chances of intercepting a device increase as there are more methods for gadgets to connect to one another. Cybercriminals can intercept protocols such as HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and API, which IoT devices use to communicate. The Internet of Things (IoT) scope does not cover only internet-connected gadgets. In addition to Bluetooth-enabled appliances, IoT security is required for all IoT devices. IoT-related data breaches have recently increased as a result of such oversights. IoT security problems continue to pose a danger to the financial security of individuals and businesses.
Remote exposure:
Due to their internet-based connection, IoT devices offer a far larger attack surface than traditional technologies. Even while this level of accessibility is highly beneficial, hackers will try to use it to remotely interact with equipment. Because of this, hacking campaigns like phishing are especially effective in stealing personal information. In order to safeguard assets, IoT security, like cloud security, must control a large number of access points.
Lack of industry foresight:
Certain sectors and their goods have also undergone digital transformations as a result of businesses’ digital transformations. To increase productivity and efficiency, industries such as transportation and healthcare have lately extended their variety of IoT devices. It has also led to a greater dependency on technology than ever before.
Reliance on technology, however, may magnify the effects of a successful data breach. These businesses are increasingly dependent on IoT devices, this is very alarming. Furthermore, It is costly and requires efforts for many healthcare and automotive companies to protect their devices. Consequently, many companies and manufacturers have been exposed to growing cybersecurity risks because of this industry-wide lack of vision.
Resource constraints:
It’s not only a matter of lack of foresight when it comes to IoT security, as newly digitalized sectors have discovered. IoT security is further hampered by the resource limitations of many of these devices. Some IoT devices do not have the processing ability to run complex firewalls or antivirus software, thus they cannot be equipped with these features. Only a few gadgets are capable of connecting with other devices at all. Bluetooth-enabled IoT gadgets, for example, have recently been the target of a wave of data breaches. Sadly, the automobile industry has been suffered the worst from this attack.
How to protect IoT systems and devices
Design your system with IoT security approaches.
A better research and development approach from the beginning of any consumer, corporate or industrial IoT device development may solve most of the security problems highlighted. Security must be enabled by default, and the latest operating systems and security hardware should be used.
It’s important for IoT developers to be aware of cybersecurity risks at every phase, not just during the design process. Fobs can be protected by placing them in a metal box or away from windows and corridors, for instance.
PKI and digital certificates
Using Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to secure client-server communications between numerous networked devices is highly recommended. PKI facilitates the encryption and decryption of private communications and interactions using digital certificates by utilizing a two-key asymmetric cryptosystem. Customer clear texts which they enter on the webpage can be privately protected. Without PKI, e-commerce would be impossible to do.
Security of the network
Threat actors can remotely manipulate IoT devices over networks. Because networks may contain digital and physical components as access points, IoT security should be able to support both of them. Antimalware, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems/intrusion prevention systems can be used in some cases to prevent threats such as unwanted IP (Internet Protocol) addresses.
API security
Most complex websites are built on APIs. These systems allow travel agencies to collect flight information from various airlines into a single database, for instance. As a result, API security needs to be protected and only authorized apps and people can access and modify data. Those things help us to ensure the accuracy of the data being transferred from IoT devices to systems. Unfortunately, hackers can breach these channels of communication. For example, T-data Mobile’s leak in 2018 is a clear illustration of what may happen. Mobile giant leaked personal data (ZIP codes, phone numbers,…) of more than 2 million users due to a “leaky API.”
 Source: https://images.ctfassets.net/3prze68gbwl1/asset-17suaysk1qa1hup/ea5bdd7b0219ffbc15d98282efa0237f/Screen-Shot-2015-04-29-at-1.49.13-PM.png
Source: https://images.ctfassets.net/3prze68gbwl1/asset-17suaysk1qa1hup/ea5bdd7b0219ffbc15d98282efa0237f/Screen-Shot-2015-04-29-at-1.49.13-PM.png
IoT security threats affect which industries the most?
From a smart house to a factory to a connected automobile, IoT security breaches may occur anywhere and in any sector. As a result, the degree of the impact varies widely depending on the system, data gathered, and/or information included.
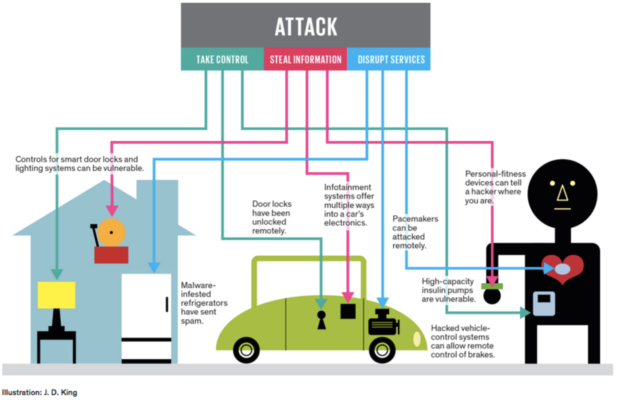
Life-threatening situations include a cyberattack that disables the brakes of a connected automobile or a hack that allows connected health equipment, such as an insulin pump, to overdose a patient. IoT-monitored refrigeration systems can be attacked, destroying medication if temperatures change. It’s also possible for attacks to have devastating consequences on key infrastructures such as an oil well, the electrical grid, or the water supply system.
The threat from other attacks, on the other hand, is not to be overlooked. A cyberattack on smart door locks, for example, may allow a thief to gain entry into a house. A hacker may also use a linked device, such as the HVAC system in Target’s example, to collect personally identifying information, causing chaos for individuals who are impacted.
Final thought
All in all, companies that apply IoT technologies must examine and manage the security threats posed by the connectivity of IoT hardware and software in order to leverage the benefits of IoT. It is necessary that they should take steps to protect their devices, their networks, and their data as soon as possible.
