We live in an era where knowledge is at our fingertips and search engines are utilized as portable libraries. During the past decade, enormous technical advancements have been made in the ways in which data and information are collected, managed, understood, presented, shared, and used. They employ a variety of tools, similar to the way the human brain works. It helps us to make information and data are linked together to produce a deeper knowledge and meaning. Analyses are recorded in the form of conceptual and cognitive maps. On the other hand, collective Intelligence acts as a type of wisdom and knowledge that emerges through a group’s experience. People working together produce a sort of intellect that simply cannot exist on an individual level, according to the notion of collective intelligence.
1. Semantic technologies
What is semantic technology?
This technique separates meanings from data and content files as well as from application code in the software. This allows both robots and humans to comprehend, share, and reason with them during execution. A new relationship or a new method to interconnect applications may be added, changed, and implemented as easily as altering the external model that the programs share with semantic technologies.
Advantages of semantic technology
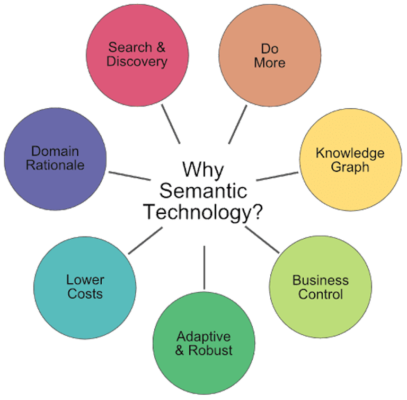
While meanings and relationships must be established in conventional information technology, they must also be “hard-wired” into data formats and application program code at design time. Humans must be involved if anything changes, information that has never been shared has to be exchanged, or two systems need to interoperate in a new way. A change cannot be made unless all parties involved have agreed on what needs to be changed and communicated it to each other. Then, the data structures and program logic must be re-coded, and these changes must be applied to both database and application. And only then, and only then, may the adjustments be made. As the name implies, semantic technologies are based on meaning. However, they can be used in a variety of contexts such as auto-recognition of themes and concepts, information and meaning-extraction, semantic data integration, and taxonomies/classification. Semantic technologies can directly search topics, concepts, and relationships that span a wide number of sources, given a specific question or query.
Source: https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/proxy/eTvCljITuCVHgrs6W82WxozLXBQOeL1e3MSsidlFhlKSJwx96AV7CNQ_lvhvz77OWhFcqkRqb02o5_V1oYPbV8x0baHCi4iUMnU0ZNtbbZsPFihfFbmaruey8MET0PKMO4O5Hwdbvf_-W_sGUgcFH8Lj31eKKT4zMJDhKg
It’s a strong tool for handling the huge quantity of nuclear data and information, especially combined with artificial intelligence, machine learning, new taxonomies, and ontologies. As an abstraction layer over current IT systems, semantic technologies enable data, content, and process integration. “Semantic Technologies” are a new level in portal interaction that enables intelligent, relevant, and responsive engagement compared to information technologies alone.
2. Collective Intelligence
What is Collective Intelligence?
When a big group of people shares their knowledge, data, and abilities to solve social problems they are referred to as a “collective intelligence” (CI). Intelligence collective refers to shared or group intelligence that comes from collaboration and competition among numerous individuals.
Collective intelligence in the workplace

Source: https://uploads-ssl.webflow.com/5fbe78003b7d531bc1ce5b26/6009a6d23bd7b015da6e3fec_2019-RETRO.png
A collective intelligence that incorporates both people and computers will be the most significant intelligence in the near future, not artificial intelligence. It’s in this area where many organizations are currently missing out on a significant opportunity. When organizations create the appropriate conditions, they can tap into a wealth of information and knowledge about their systems, processes, goods, and services to boost productivity and innovation. This collective intelligence and its many commercial benefits are valued by leaders who appreciate the experience, knowledge, and insight potential that employees have accumulated over many years of employment. So, they are providing their employees a voice in the business, which is a vital element of an employee-engaged workplace.
Benefits of collective intelligence:
1. Collective intelligence improves the performance of a team. Because a new level of knowledge arises when diverse minds join together. If a team is working on a presentation to impress a new customer, each member of the team will provide something known as general individual intelligence, but when combined, it will generate something known as a general collective intelligence factor. In this way, the group will be able to operate at a much higher level.
2. As a result of collective intelligence, new markets can be created.
Collaboration enhances group intelligence, making ideas and alternatives more inventive and successful. With many diverse people engaged, group intelligence improves. As part of a collective intelligence collecting effort, collective intelligence may potentially assist create new markets for products.
3. Productivity is increased through collective intelligence. An organization’s productivity can be improved if employees believe they have a voice that is truly heard. It has been demonstrated that individuals perform better when they have the opportunity to make decisions about their working conditions as a result of flexibility and the capacity to adjust to their environment.
4. Coordination is strengthened through collective intelligence. Employees are able to come up with new, more efficient ways to do tasks. Managers save time and may focus on other things as a result of this, while also reducing transaction costs.
5. Reducing expenses can be achieved by collective intelligence. Open source or free software allows companies to produce better products in less time. There’s little doubt that a big group of highly trained individuals working on the same problem can solve a product more rapidly and for less money than if the firm tried to accomplish this on its own.
In summary, to handle different types of uncertainty, collective intelligence relies on a combination of data, technology, and varied human talents.
