Currently, there is a need for an immediate answer to a problem. There are useful ways and tools to help with that. This has taken Wearables, Body Sensor Networks, and Smart Portable Devices from nothing to ubiquitous. It has no signs of stopping down and an ever-increasing social effect. This article will analyze each issue of Wearables, Body Sensor Networks, and Smart Portable Devices.
1. Wearables
- What are wearables?
It’s a little gadget that’s far more portable than a phone, and you can simply carry it on your person as an accessory. It is wearable, embedded in clothing, tattooed on the skin or implanted in the user’s body. Compared with mobile phones, it has many advantages, such as: lightweight and fast, low energy consumption, advanced interaction features, design simplification, etc.
It is a combination of an internet connection and a microprocessor. Therefore, you constantly receive real-time messages/notifications through it since it is connected to the Internet and immediately connects to mobiles and personal computers. It enables you to access data from anywhere.
Wearables are diverse and popular, such as fitness activity trackers, smartwatches, Bluetooth headsets, smartwatches, web-enabled glasses, virtual reality and augmented reality headsets.
- Benefits of wearables
Monitoring: monitoring chips with built-in GPS to monitor children and the elderly.
Smart tattoos contain flexible electronic sensors to help monitor muscle function, sleep disorders, and heart and brain activity. In addition, it can be used to authenticate data transmission to smartphones or scanners to speed up processing processes.
Safety wearables: used as casual wear. However, when there is a threat or danger, it will issue a warning, turn on a loud alarm, and send a notification (a pre-set message, a recorded voice message with the location of where the device is located with built-in GPS) to someone (friend, family, police, or someone in the ecosystem using the device).
Improve health: helps you keep track of your daily activities, such as how long you sleep, your heart rate, and the number of steps you take. From there, it will analyze trends and give advice on activities.
Smartwatches: it will be synced with your smartphone. It helps you to receive/send notifications, emails, messages, and phone calls. It also integrates fitness trackers. At the same time, it helps to monitor and detect diseases early so that there is better treatment for each individual.
Portable and hands-free: with its compact and portable size, it helps to perform operations quickly.
- Real-life Examples of wearables
iTBra: developed by Cyrcadia Health. It is an intelligent patch using collected data. It provides analysis to detect early signs of breast cancer.
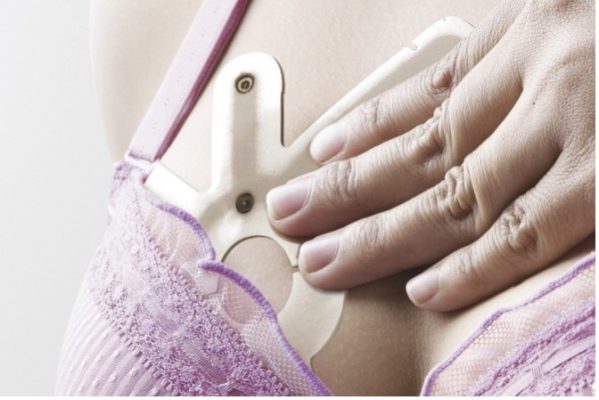 Figure 1: iTBra (source: Hi-tech iTBra a breakthrough for Asian women at high risk of breast cancer | South China Morning Post (scmp.com))
Figure 1: iTBra (source: Hi-tech iTBra a breakthrough for Asian women at high risk of breast cancer | South China Morning Post (scmp.com))
AIR Louisville: wearable devices in Louisville, Kentucky. The devices collect data on air quality, fine dust, and pollution from which to give warnings about hazardous areas.

Figure 2: AIR Louisville (source: AIR Louisville – Results (airlouisville.com))
Misfit, Basis and Fitbit are prime examples of the benefits of fitness trackers.

Figure 3: Misfit fitness trackers (source: Misfit Ray Review: Best Fitness Tracker Under £50 (techadvisor.com))
The popular smartwatch is the Apple Watch, which is synced with the iPhone. Android Wear, for example, Moto 360, Samsung Gear, only connects to phones running the Android operating system. A Pebble is a device that can be synced with any mobile operating system.
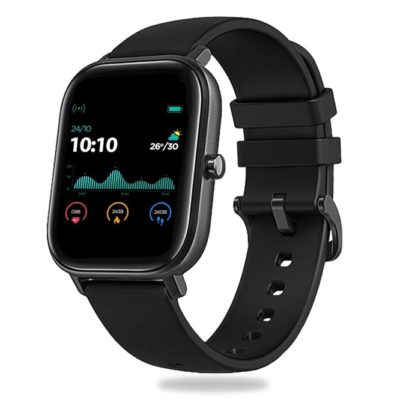

Figure 4: Pebble smartwatch (source: Pebble Pace Smart Watch with Oximeter Function for SpO2 (Blood Oxygen) Monitoring with Full Touch Dynamic Colour Display, Multiple Sports Mode, HR, Sleep and BP Monitoring (Black) : Amazon.in: Electronics (amazon.in))
MagicBand: Disney helps users pay, guides them to hotel rooms, and gives them access to rides.
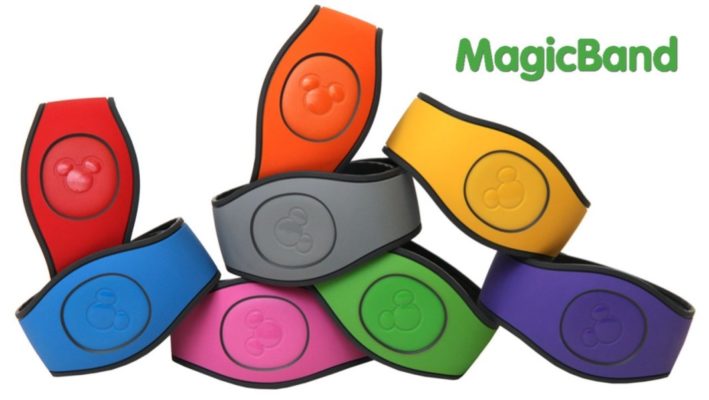

Figure 5: MagicBand (source: MagicBand 2 Coming to Walt Disney World Resort | Disney Parks Blog (go.com))
Nokia developed Vibrating Tattoos that will vibrate when a message or call is made.
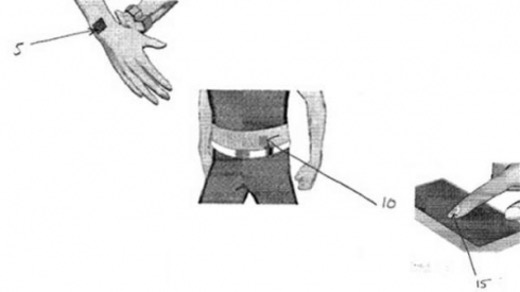
Figure 6: Vibrating Tattoos (source: Vibrating Tattoo Patented By Nokia | TheLast Newspaper (thelastnewspaper.com))
- Future of wearables
The combination of miniaturized microprocessors, high-speed data transfer and mobile networks is driving the growth of wearables.
In the future, towards the development of specialized and practical products.
Wireless charging would be a good solution to improve the battery life of current wearables. Batteries can be charged from sources such as solar energy, body heat and movement into power. When the batteries of today’s devices can only be used for almost a day.

Figure 7: Wireless charging (source: Shipments of Smartphones with Wireless Charging-Capability Surge – EE Times Asia (eetasia.com))
Measure data accuracy: improves the accuracy of the device. Especially in healthcare applications, the collected data must be of optimal accuracy before the analysis is meaningful.
Security and privacy: data is not encrypted and is transmitted via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connections. In the future, data needs to be more secure, especially personal information. The adjustment of the security protocol in the D2D network needs to be researched and developed.
Authentication: The microchip uses a combination of radio-frequency identification (RFID) and near-field communication (NFC) technology used to uniquely identify users instead of usernames and passwords. This also integrates features such as helping users make payments and unlocking.
Lower visibility: this will make devices look like jewelry, clothing, patches, or straps.
Use machine learning in data collection and analysis.
Data transmission: using 5G and other technologies to increase transmission speed. Moving data storage, processing, and management from the centralized cloud to edge computing enables real-time data collection and processing, enabling faster and more efficient responses. Compressive sensing helps to optimize energy consumption and efficient bandwidth. These are the 2 most important elements in wearables.
Localization: wearable devices mainly rely on wireless networks (BLE, Wi-Fi, UWB) which are vulnerable to Non-Line of-Sight (NLOS), multipath propagation, scattering, diffraction, and reflection leading to information transmission incorrect. In the future, there will be a need for technologies to improve this situation.
2. Body Sensor Networks
-
- What are Wireless Sensor Networks?
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) are advancements in energy storage, sensor design, and wireless communication. It helps to monitor many environmental factors, such as magnetic field, tilt and vibration, light intensity, barometric pressure, humidity, and temperature.
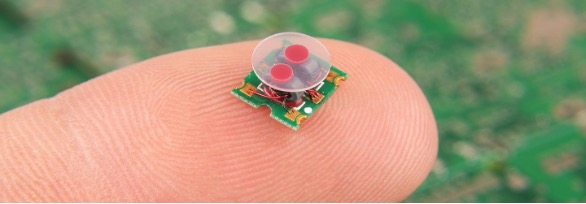
Figure 8: Smart Dust defense project allows to monitor enemy movements secretly (source: Smart Dust Could Ramp Up Internet of Things in Higher Education | EdTech Magazine (edtechmagazine.com))
WSN was developed based on an open-source called Tiny Microthreading Operating System (TinyOS), which is an energy-efficient operating system. TinyOS performs controlling power dissipation, routing decisions, and sensor measurements.
WSN applications are divided into 3 categories: monitoring objects, monitoring environments, and monitoring the interaction of these objects with environments.
- Overview Body Sensor Networks
The Body Sensor Network (BSN) is the attachment of sensors to the surface of the body as well as implanting them into tissues. It contributes to the establishment of a consistent strategy for ubiquitous monitoring by establishing a standard.
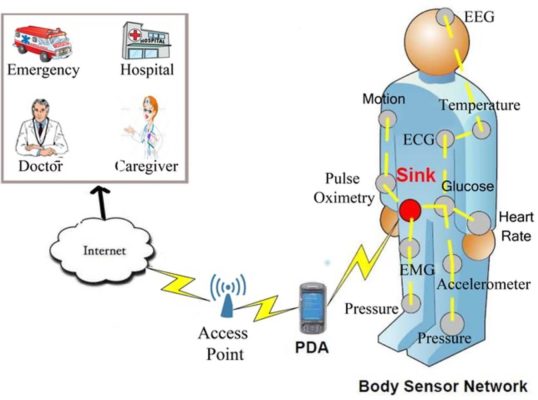
Figure 9: An example of Body Sensor Network (source: (PDF) An Efficient Next Hop Selection Algorithm for Multi-Hop Body Area Networks (researchgate.net))
The architecture of the BSN will include a number of sensors (battery, wireless transmitter, a small processor) that are attached to the body and connected to the hospital, office and home. The nodes of the BSN collect data from the sensors they connect to, do low-level processing of the data, and then wirelessly transmit the information to the Local Processing Unit (LPU) for processing and consolidation. Finally, the data is sent to the central monitoring server via (3G, GPRS, Bluetooth or wireless LAN).
- The function of Body Sensor Networks
Wireless BSNs provides a framework for establishing such a health monitoring system and diagnostic tools. It will provide dramatic, important information.
Monitoring Patients with Chronic Disease: detect early signs of chronic diseases (heart through ECG, high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus) to prevent the risk of stroke. As well as monitoring the patient’s response and progress to different treatments.
Monitoring Hospital Patients: automate patient monitoring from anywhere. Monitoring and detecting problems that occur after surgery is very important. This also provides a streamlined and optimal process for receiving and dealing with the patient’s condition.
Monitoring elderly patients: this helps provide the elderly with adequate and timely medical help. The benefits are reduced mortality, morbidity and the need for hospitalization.
Some of the other benefits of BSN also apply to areas including security, military and sports.
- Real-life Examples of Body Sensor Networks
The implantable biosensor chip developed by EPFL integrated Systems Laboratory is implanted on the skin surface. Connected to a smartphone to measure multiple biochemistry indicators at the same time. This helps keep track of cholesterol, glucose and drug concentrations.

Figure 10: Biosensor chip (source: Implantable biosensor chip can monitor glucose and drugs in real-time – SlashGear (slashgear.com))
European Commission “Wealthy”: devices embedded in clothing, by incorporating them onto a textile platform to achieve universal surveillance.
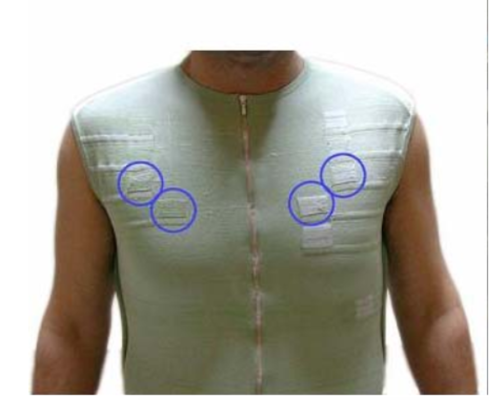
Figure 11: European Commission “Wealthy” (source: Guang-Zhong Yang, Body Sensor Networks, Springer 2006, p.12)
CardioMEMS: developed implantable pressure sensors that can measure the pressure after being implanted into an aneurism sac during the endovascular repair.
Figure 12: CardioMEMS (source: New Long-term Data Published in The Lancet Further Demonstrates Superiority of the CardioMEMS HF System over Standard of Care | Business Wire (businesswire.com))
- Challenge and Opportunity of Body Sensor Networks
Data Transfer: improves data loss to ensure real-time data interrogation capabilities and QoS.
Wireless Technology: uses low power and ensures signal transmission under extreme circumstances.
Context Awareness: full awareness of the human body’s adaptation to a changing context.
Access: ensures easy sensor change and device biodegradability.
Power Demand: still works normally when the power supply is weak or insufficient.
Data Protection: data security needs to be ensured to avoid revealing sensitive information to the outside.
Event Detection: has a mechanism to detect abnormal changes in the body.
Dynamics: devices are more exposed to the environment and ensure the quality of operation when the body is active.
Node Size: needs to be reduced in size or maybe hidden undetectable.
Node Accuracy: the accuracy of data collection of nodes must be improved, then the analysis makes new predictions meaningful.
Node Function: integrates multiple tasks into the same sensor.
Node Number: reduces the number of necessary nodes that need to be used.
3. Smart Portable Devices
-
- Introduction Smart Portable Devices
Smart Portable Devices are compact, extremely lightweight devices that you can easily carry and keep. The device is battery-powered and has components such as storage, memory, a CPU and access to the internet. The operating systems under development for Smart Portable Devices are iOS, Android, Windows, Lune OS, etc.
A smartphone or handheld computer is a portable unit that includes smartphones, tablets, laptops, video cameras, removable hard disks, USB drives, etc.

Figure 13: Smart Portable Devices (source: Mobile Portable Devices Icon Set Symbol Flat Style Vector Illustration. Royalty Free Cliparts, Vectors, And Stock Illustration. Image 79873938. (123rf.com))
- Advantage of Smart Portable Devices
Communication: it is undeniable that Smart Portable Devices help users to connect and communicate strongly in real time to receive and solve important problems related to studies, work, health, etc. This is really meaningful in the healthcare industry. Through the process of collecting and analyzing data, users can understand their current health status. It also helps doctors to have an overview of the condition from which to give appropriate treatment. Minimize the risk that it will happen.
Higher efficiency and productivity: by using devices, it is possible to make the most of space and time to solve problems. Offer optimal plans. You can access your data anytime and anywhere from your workplace, company, factory, etc.
Accept payments wirelessly: make convenient payment transactions without having to go to transaction points like before. This saves travel time and integrates many convenient payment services with just one click of a button, and you can successfully transact, such as buying movie tickets, paying electricity/water. Contributing to promoting digital transformation in many industries. In particular, it brought the e-commerce industry to develop rapidly.
The advantages of Smart Portable Devices pervade all areas of life. According to a statistic, up to 95% of the world’s population uses one or more Smart Portable Devices. This proves to be an extremely large community of users because it brings very significant benefits.
- Real-life Examples of Smart Portable Devices
Smartphones: are the most popular mobile devices. It can replace the needs of a laptop or tablet. It can help you play games, watch movies, compose reports, transfer money, create websites and more.

Figure 14: Smartphones (source: Smartphones account for 59% of all spending on consumer electronics in 2018: tech author – NotebookCheck.net News (notebookcheck.net))
Laptops: are devices that serve the daily study and work needs of anyone, anytime and anywhere. You can optimize your time and workspace with your laptop.

Figure 15: Laptops (source: The Best Laptops You Can Buy | Time (time.com))
Smartwatches: are a new device born in recent years, but they have a significant development with a lot of utilities, from sending/receiving notifications, alerts, accessing the internet, and making connections with smartphones and personal laptops multiply. Bringing the Smart Portable Devices market to a new level of development.

Figure 16: Apple and Android smartwatches (source: The best Apple and Android smartwatches of 2021 | NextPit (nextpit.com))
Power banks or portable chargers: the use of Smart Portable Devices requires charging anytime and anywhere. Not only that, it requires a fast and convenient charging speed.

Figure 17: Portable chargers (source: The Best Portable Chargers and Power Banks for 2021 | PCMag (pcmag.com))
Muse: is the Brain Sensing Headband that helps monitor brain activity and transmits data to a smartphone, computer or tablet via Bluetooth. This device helps you reduce stress, and monitors brain activity in real-time to give the advice to help you calm down.

Figure 18: Muse (source: Muse™ – Meditation Made Easy with the Muse Headband (choosemuse.com))
LARQ: is a Smart Self-Cleaning Water Bottle. That’s right, it allows you to filter clean water at any time when you press the button. The water cleaning process will take place very quickly and continuously if you set this mode.

Figure 19: LARQ bottle (source: LARQ Review – Is the Self-Cleaning Water Bottle Worth £109? (discerningcyclist.com))
- Future development potential of Smart Portable Devices
Small Microprocessor: components are connected closer together to reduce energy use, save battery capacity, and integrate heat-removing tiny fans.
Accelerate data transmission (research to find alternatives to GPRS, 4G) to provide continuous information in real-time, allowing rapid data transmission.
Qualcomm Snapdragon processors are required for complex portable devices that demand a graphical user interface and wireless connection.
Real-time operating system development and applications are combined with advanced features and are highly customizable.
Use IoT to connect devices together. It simultaneously communicates with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth/BLE, Near Field Radio, and through mobile-cellular networks.
Wearable Technology: a future technology that brings significant convenience to Smart Portable Devices. It offers flexibility and promising performance.
5G: will be the future of Smart Portable Devices. It helps to make a reliable connection and has a larger transmission bandwidth. Connection loss can not occur.
Stretchable Screens and Foldable: Using a large screen to work is very convenient and convenient. However, carrying and moving will be very difficult. This will be the future trend to meet the increasing demands of customers.

Figure 20: Closed Book can foldable (source: From Foldable Phones to Stretchy Screens – IEEE Spectrum (spectrum.ieee.org))
4. Conclusion
In the future, we are entering an era of breakthrough technology. That place is where Wearables, Body Sensor Networks, and Smart Portable Devices have become popular to serve all the needs of society. Currently, the development potential of these fields is enormous. There are many opportunities, but there are certain challenges. It is important to understand and grasp the next trend to make a reasonable choice for yourself.
Source of references:
- 18 Portable Health Gadgets That Can Change Your Life (travelaway.me)
- A Survey on Wearable Technology: History, State-of-the-Art and Current Challenges – ScienceDirect (sciencedirect.com)
- A Quick Guide to Portable Medical Devices (einfochips.com)
- Future of Smart Phones – 2021 – Brought to you byITChronicles (itchronicles.com)
- Guang-Zhong Yang, Body Sensor networks, Springer 2006.
- Portable devices we cannot afford to miss in the present-day scenario – Primopreneur (primopreneur.com)
- Wearables: What is the Apple Watch? (gcfglobal.org)
- Wearable Technology Definition (investopedia.com)
- what are portable devices? List all common portable devices | ssla.co.uk (ssla.co.uk)
